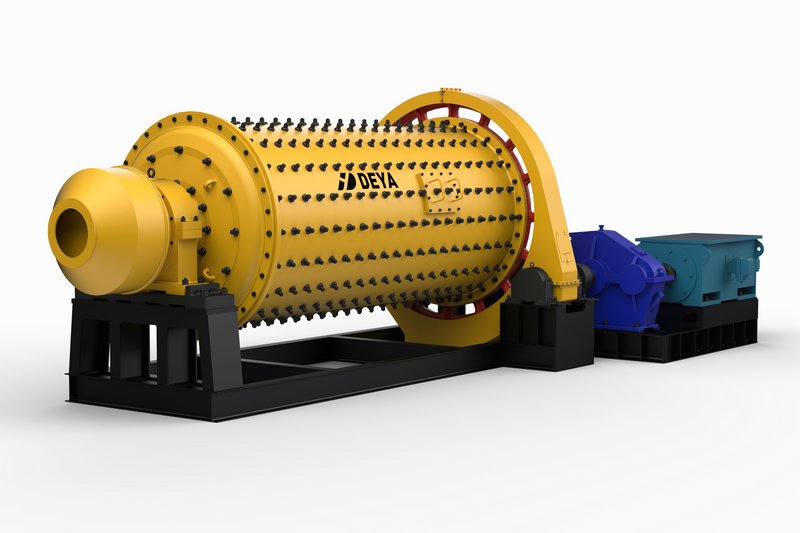
Introduction
A ball mill is a type of grinder used to grind or blend materials for use in mineral dressing processes, paints, pyrotechnics, ceramics, cement, etc. It works on the principle of impact and attrition: size reduction is done by impact as the balls drop from near the top of the shell.
The final stages of comminution are performed in tumbling mills using steel balls as the grinding medium and so designated “ball mills.” In the mineral dressing plant, only the grate ball mill and overflow ball mill are widely used. Click here to know more about ball mill machine.
Working principle
As a construction, a ball milling device usually consists of a cylindrical vessel mounted on an appropriate basis at both ends which allows rotation of the vessel around the center axis.
The mill is driven by a girth gear bolted to the shell of the vessel and a pinion shaft moved by a prime mover. The prime movers are usually synchronous motors equipped with an air clutch or gear transmission.
After the mill is charged with the starting materials, like ore, rock, etc., and the grinding media, typically steel balls, the milling process takes place during rotation as a result of the transfer of kinetic energy of the moving grinding media into the grinding product.
Applications
The applications of ball mills are ubiquitous in mineral processing and mining industry, metallurgy, cement production, chemical industry, pharmaceutics and cosmetics, ceramics, different kinds of laboratory studies and tests. Besides particle size reduction, ball mills are also widely used for mixing, blending and dispersing, amorphisation of materials and mechanical alloying.
Factors that affect ball mill capacity
Ball mill size reduction depends on the following basic factors
1. Characteristics of the material charged in the mill, like mass, volume, hardness, density and size distribution of the charge
2. Characteristics of the grinding media, like mass, density, ball size distribution
3. Speed of rotation of the ball mill
4. Slurry density in case of wet grinding operation
An important characteristic of an industrial ball mill is its production capacity which is measured in tons of production per hour. The production capacity depends on mill dimensions, the type of the mill, overflow or grate discharge, the speed of rotation, the mill loading, the final product size required from a given feed size, the work index of the material, the mill shaft power and the specific gravity of the material.
Technical data
| Model | Rotation speed | Grind media quantity | Feed size | Discharge size | Capacity | Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPM | Ton | mm | mm | T/H | Kw | |
| Ф1200×2400 | 36 | 3 | ≤25 | 0.075-0.6 | 1.5-4.8 | 30 |
| Ф1200×3000 | 36 | 3.5 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 1.6-5 | 37 |
| Ф1200×4500 | 32.4 | 5 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 1.6-5.8 | 55 |
| Ф1500×3000 | 29.7 | 7.5 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 2-5 | 75 |
| Ф1500×4500 | 27 | 11 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 3-6 | 110 |
| Ф1500×5700 | 28 | 12 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 3.5-6 | 130 |
| Ф1830×3000 | 25.4 | 11 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 4-10 | 130 |
| Ф1830×4500 | 25.4 | 15 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 4.5-12 | 155 |
| Ф1830×6400 | 24.1 | 21 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 6.5-15 | 210 |
| Ф1830×7000 | 24.1 | 23 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 7.5-17 | 245 |
| Ф2100×3000 | 23.7 | 15 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 6.5-36 | 155 |
| Ф2100×4500 | 23.7 | 24 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 8-43 | 245 |
| Ф2100×7000 | 23.7 | 26 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 8-48 | 280 |
| Ф2200×4500 | 21.5 | 27 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 9-45 | 280 |
| Ф2200×6500 | 21.7 | 35 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 14-26 | 380 |
| Ф2200×7000 | 21.7 | 35 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 15-28 | 380 |
| Ф2200×7500 | 21.7 | 35 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 15-30 | 380 |
| Ф2400×3000 | 21 | 23 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 7-50 | 245 |
| Ф2400×4500 | 21 | 30 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 8.5-60 | 320 |
| Ф2700×4000 | 20.7 | 40 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 12-80 | 380 |
| Ф2700×4500 | 20.7 | 48 | ≤25 | 0.074-0.4 | 12-90 | 480 |
Note: Base on different materials, feed size, material abrasiveness and other factors, the data will be different. Contact Deya team for more information.